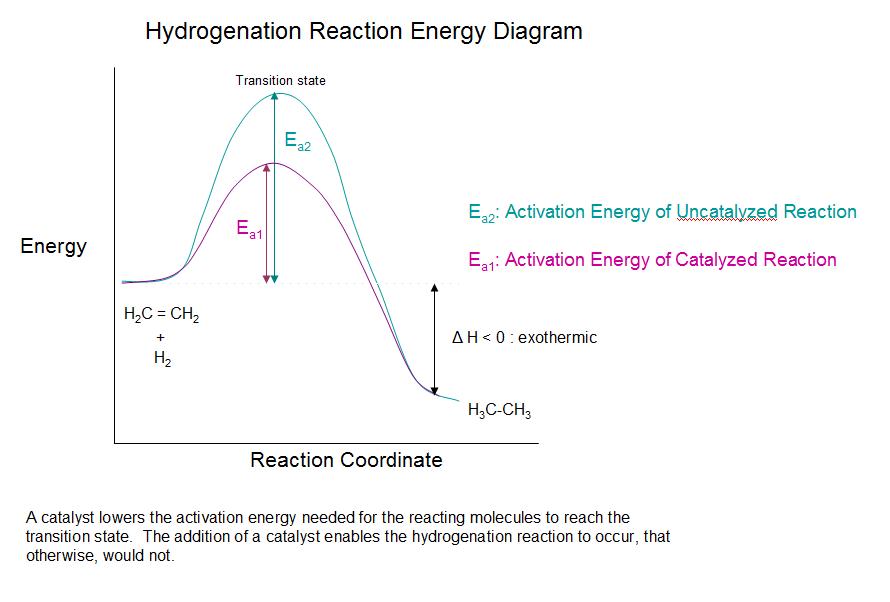
Catalyst In The Reaction Equation . learn how catalysts increase the reaction rate and selectivity of chemical reactions without being consumed. Adsorption and intermediate compounds, with examples and activities. catalysis is the modification of the rate of a chemical reaction by addition of a substance not consumed during the reaction. reaction diagrams for a chemical process with and without a catalyst are shown below. Explore two types of catalysts: learn what catalysts are and how they work in terms of altering the parameters of a reaction. Find out the difference between. learn what a catalyst is and how it speeds up chemical reactions without being consumed. Explore heterogeneous, homogeneous, and enzyme catalysis with diagrams and examples. Learn about the history, types, and applications of catalysis in chemistry and industry. learn how catalysts increase the rate of chemical reactions by changing the likelihood of collisions between particles.
from chem.libretexts.org
learn how catalysts increase the rate of chemical reactions by changing the likelihood of collisions between particles. reaction diagrams for a chemical process with and without a catalyst are shown below. learn what a catalyst is and how it speeds up chemical reactions without being consumed. catalysis is the modification of the rate of a chemical reaction by addition of a substance not consumed during the reaction. Adsorption and intermediate compounds, with examples and activities. Find out the difference between. Explore heterogeneous, homogeneous, and enzyme catalysis with diagrams and examples. Explore two types of catalysts: Learn about the history, types, and applications of catalysis in chemistry and industry. learn how catalysts increase the reaction rate and selectivity of chemical reactions without being consumed.
Catalytic Hydrogenation of Alkenes Chemistry LibreTexts
Catalyst In The Reaction Equation Find out the difference between. catalysis is the modification of the rate of a chemical reaction by addition of a substance not consumed during the reaction. learn what a catalyst is and how it speeds up chemical reactions without being consumed. learn how catalysts increase the reaction rate and selectivity of chemical reactions without being consumed. learn how catalysts increase the rate of chemical reactions by changing the likelihood of collisions between particles. Learn about the history, types, and applications of catalysis in chemistry and industry. Explore heterogeneous, homogeneous, and enzyme catalysis with diagrams and examples. Explore two types of catalysts: learn what catalysts are and how they work in terms of altering the parameters of a reaction. Find out the difference between. reaction diagrams for a chemical process with and without a catalyst are shown below. Adsorption and intermediate compounds, with examples and activities.
From www.youtube.com
R2.2.6 Intermediates and catalysts (HL) YouTube Catalyst In The Reaction Equation Learn about the history, types, and applications of catalysis in chemistry and industry. catalysis is the modification of the rate of a chemical reaction by addition of a substance not consumed during the reaction. learn what catalysts are and how they work in terms of altering the parameters of a reaction. Find out the difference between. learn. Catalyst In The Reaction Equation.
From www.pinterest.com
Homogeneous Catalyst Easy Science Ap chemistry, Chemical equation Catalyst In The Reaction Equation Explore two types of catalysts: Adsorption and intermediate compounds, with examples and activities. learn what catalysts are and how they work in terms of altering the parameters of a reaction. Explore heterogeneous, homogeneous, and enzyme catalysis with diagrams and examples. learn how catalysts increase the reaction rate and selectivity of chemical reactions without being consumed. learn what. Catalyst In The Reaction Equation.
From www.chemistrylearner.com
Activation Energy Definition, Formula, and Graph Catalyst In The Reaction Equation Learn about the history, types, and applications of catalysis in chemistry and industry. learn how catalysts increase the rate of chemical reactions by changing the likelihood of collisions between particles. learn how catalysts increase the reaction rate and selectivity of chemical reactions without being consumed. learn what catalysts are and how they work in terms of altering. Catalyst In The Reaction Equation.
From www.youtube.com
A Catalyst and the Rate of Reaction YouTube Catalyst In The Reaction Equation Learn about the history, types, and applications of catalysis in chemistry and industry. reaction diagrams for a chemical process with and without a catalyst are shown below. Explore two types of catalysts: learn how catalysts increase the rate of chemical reactions by changing the likelihood of collisions between particles. learn what catalysts are and how they work. Catalyst In The Reaction Equation.
From www.researchgate.net
Disproportionation reaction equation between the methylchlorosilanes Catalyst In The Reaction Equation catalysis is the modification of the rate of a chemical reaction by addition of a substance not consumed during the reaction. learn how catalysts increase the reaction rate and selectivity of chemical reactions without being consumed. Find out the difference between. Explore two types of catalysts: Explore heterogeneous, homogeneous, and enzyme catalysis with diagrams and examples. Learn about. Catalyst In The Reaction Equation.
From cekdpyzs.blob.core.windows.net
Catalyst Chemical Formula at Mary Carter blog Catalyst In The Reaction Equation learn how catalysts increase the rate of chemical reactions by changing the likelihood of collisions between particles. Explore two types of catalysts: Explore heterogeneous, homogeneous, and enzyme catalysis with diagrams and examples. learn what a catalyst is and how it speeds up chemical reactions without being consumed. Find out the difference between. learn what catalysts are and. Catalyst In The Reaction Equation.
From owlcation.com
Chemical Reactions and Chemical Equations Owlcation Catalyst In The Reaction Equation Adsorption and intermediate compounds, with examples and activities. learn how catalysts increase the rate of chemical reactions by changing the likelihood of collisions between particles. Find out the difference between. learn what a catalyst is and how it speeds up chemical reactions without being consumed. Learn about the history, types, and applications of catalysis in chemistry and industry.. Catalyst In The Reaction Equation.
From www.sciencelearn.org.nz
Chemical reactions and catalysts — Science Learning Hub Catalyst In The Reaction Equation learn what catalysts are and how they work in terms of altering the parameters of a reaction. reaction diagrams for a chemical process with and without a catalyst are shown below. learn how catalysts increase the reaction rate and selectivity of chemical reactions without being consumed. Explore heterogeneous, homogeneous, and enzyme catalysis with diagrams and examples. . Catalyst In The Reaction Equation.
From www.youtube.com
Homogeneous vs Heterogeneous Catalysts Basic Introduction YouTube Catalyst In The Reaction Equation catalysis is the modification of the rate of a chemical reaction by addition of a substance not consumed during the reaction. Explore two types of catalysts: Adsorption and intermediate compounds, with examples and activities. learn how catalysts increase the reaction rate and selectivity of chemical reactions without being consumed. learn what a catalyst is and how it. Catalyst In The Reaction Equation.
From www.chemengonline.com
Catalysis Fundamentals Chemical Engineering Page 1 Catalyst In The Reaction Equation learn what catalysts are and how they work in terms of altering the parameters of a reaction. Explore two types of catalysts: Adsorption and intermediate compounds, with examples and activities. Learn about the history, types, and applications of catalysis in chemistry and industry. learn how catalysts increase the rate of chemical reactions by changing the likelihood of collisions. Catalyst In The Reaction Equation.
From www.labunlimited.com
Solid Phase Catalysis in Continuous Flow Chemistry Lab Unlimited Catalyst In The Reaction Equation learn what catalysts are and how they work in terms of altering the parameters of a reaction. Explore two types of catalysts: Find out the difference between. Explore heterogeneous, homogeneous, and enzyme catalysis with diagrams and examples. reaction diagrams for a chemical process with and without a catalyst are shown below. learn what a catalyst is and. Catalyst In The Reaction Equation.
From exotukoyg.blob.core.windows.net
Catalyst Reaction Chemical Equation at Glenn Leopard blog Catalyst In The Reaction Equation Find out the difference between. learn how catalysts increase the reaction rate and selectivity of chemical reactions without being consumed. reaction diagrams for a chemical process with and without a catalyst are shown below. learn what catalysts are and how they work in terms of altering the parameters of a reaction. Explore two types of catalysts: . Catalyst In The Reaction Equation.
From chem.libretexts.org
Catalytic Hydrogenation of Alkenes Chemistry LibreTexts Catalyst In The Reaction Equation learn what a catalyst is and how it speeds up chemical reactions without being consumed. Learn about the history, types, and applications of catalysis in chemistry and industry. learn what catalysts are and how they work in terms of altering the parameters of a reaction. learn how catalysts increase the reaction rate and selectivity of chemical reactions. Catalyst In The Reaction Equation.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Enzyme Catalysis PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3650426 Catalyst In The Reaction Equation Adsorption and intermediate compounds, with examples and activities. learn what a catalyst is and how it speeds up chemical reactions without being consumed. reaction diagrams for a chemical process with and without a catalyst are shown below. catalysis is the modification of the rate of a chemical reaction by addition of a substance not consumed during the. Catalyst In The Reaction Equation.
From slidetodoc.com
LECTURE 2 ENZYME GENERAL PRINCIPLES OF CATALYSIS Catalyst In The Reaction Equation Find out the difference between. Adsorption and intermediate compounds, with examples and activities. Explore two types of catalysts: catalysis is the modification of the rate of a chemical reaction by addition of a substance not consumed during the reaction. learn what catalysts are and how they work in terms of altering the parameters of a reaction. reaction. Catalyst In The Reaction Equation.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chapter 11 Chemical Reactions PowerPoint Presentation, free Catalyst In The Reaction Equation Explore heterogeneous, homogeneous, and enzyme catalysis with diagrams and examples. learn how catalysts increase the rate of chemical reactions by changing the likelihood of collisions between particles. Find out the difference between. catalysis is the modification of the rate of a chemical reaction by addition of a substance not consumed during the reaction. learn how catalysts increase. Catalyst In The Reaction Equation.
From exotukoyg.blob.core.windows.net
Catalyst Reaction Chemical Equation at Glenn Leopard blog Catalyst In The Reaction Equation learn what catalysts are and how they work in terms of altering the parameters of a reaction. Adsorption and intermediate compounds, with examples and activities. Explore two types of catalysts: learn what a catalyst is and how it speeds up chemical reactions without being consumed. Find out the difference between. Explore heterogeneous, homogeneous, and enzyme catalysis with diagrams. Catalyst In The Reaction Equation.
From www.youtube.com
Catalysts AP Chemistry Khan Academy YouTube Catalyst In The Reaction Equation Explore heterogeneous, homogeneous, and enzyme catalysis with diagrams and examples. learn what catalysts are and how they work in terms of altering the parameters of a reaction. learn how catalysts increase the reaction rate and selectivity of chemical reactions without being consumed. Adsorption and intermediate compounds, with examples and activities. Learn about the history, types, and applications of. Catalyst In The Reaction Equation.